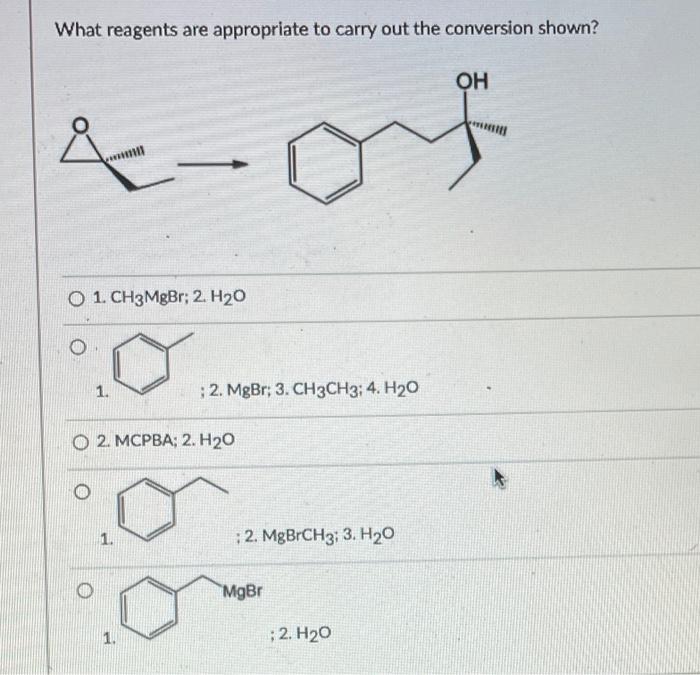
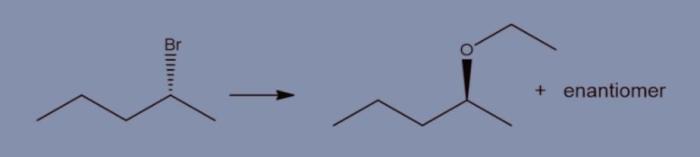
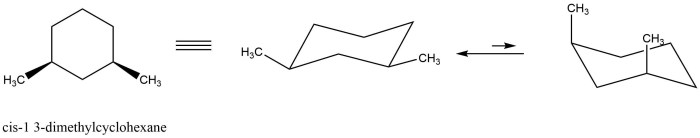
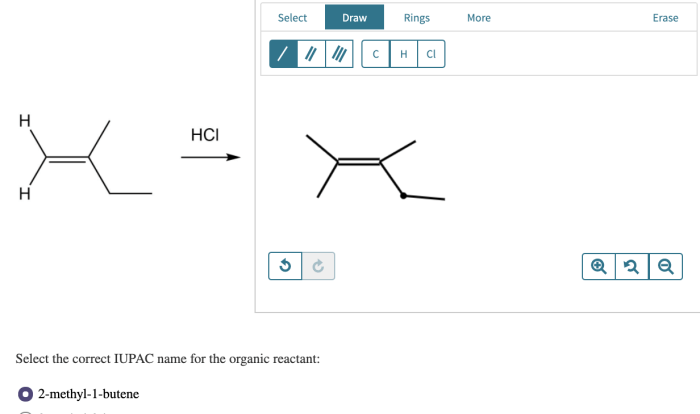
What reagents are appropriate to carry out the conversion shown – The question of what reagents are appropriate to carry out a given conversion is a fundamental one in organic synthesis. The choice of reagents can have a profound impact on the reaction outcome, including the yield, selectivity, and reaction time.
In this article, we will discuss the factors that need to be considered when selecting reagents for a given conversion, and we will provide a table of commonly used reagents and their applications.
The second paragraph provides more specific information about the factors that need to be considered when selecting reagents. These factors include the functional groups present in the starting material and the product, the reaction conditions, and the desired yield and selectivity.
Reagent Types: What Reagents Are Appropriate To Carry Out The Conversion Shown
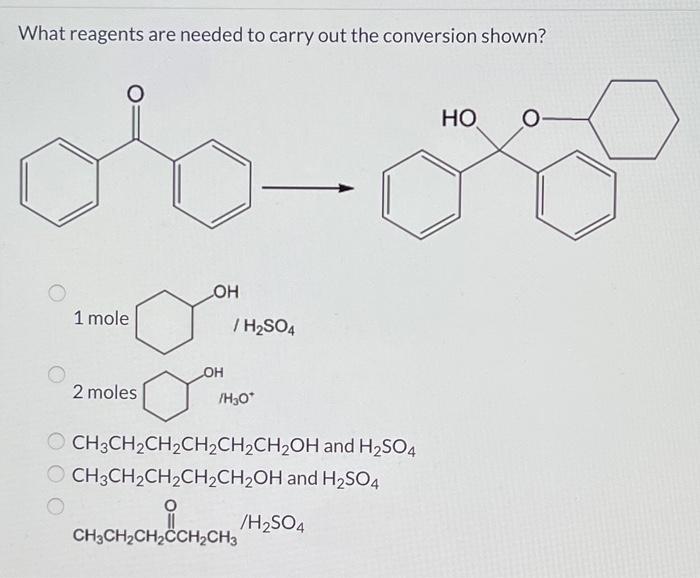
Reagents are substances that are used to bring about chemical reactions. In organic synthesis, a wide variety of reagents are available, each with its own unique reactivity and selectivity. The choice of reagent is critical to the success of a reaction, as it can influence the reaction pathway, yield, and product distribution.
Commonly Used Reagents, What reagents are appropriate to carry out the conversion shown
- Nucleophiles:Nucleophiles are species that donate electrons to an electrophile, forming a new covalent bond. Common nucleophiles include hydroxide ion (OH –), alkoxide ion (RO –), and Grignard reagents (RMgX).
- Electrophiles:Electrophiles are species that accept electrons from a nucleophile, forming a new covalent bond. Common electrophiles include alkyl halides (R-X), carbonyl compounds (R 2C=O), and imines (R 2C=NR).
- Bases:Bases are substances that donate protons (H +), accepting electrons in return. Common bases include sodium hydroxide (NaOH), potassium tert-butoxide (t-BuOK), and pyridine (C 5H 5N).
- Acids:Acids are substances that donate protons (H +), releasing electrons in return. Common acids include hydrochloric acid (HCl), sulfuric acid (H 2SO 4), and trifluoroacetic acid (CF 3COOH).
- Oxidizing agents:Oxidizing agents are substances that accept electrons, causing the oxidation of another species. Common oxidizing agents include potassium permanganate (KMnO 4), sodium dichromate (Na 2Cr 2O 7), and hydrogen peroxide (H 2O 2).
- Reducing agents:Reducing agents are substances that donate electrons, causing the reduction of another species. Common reducing agents include sodium borohydride (NaBH 4), lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH 4), and zinc (Zn).
Reagent Selection
The choice of reagent is critical to the success of a reaction. The following factors should be considered when selecting a reagent:
- Reactivity:The reactivity of a reagent refers to its ability to undergo a reaction. The reactivity of a reagent can be affected by its structure, polarity, and steric hindrance.
- Selectivity:The selectivity of a reagent refers to its ability to react with a specific functional group or to form a specific product. The selectivity of a reagent can be affected by its structure, polarity, and steric hindrance.
- Functional group compatibility:The functional group compatibility of a reagent refers to its ability to react with a specific functional group without affecting other functional groups. The functional group compatibility of a reagent can be affected by its structure, polarity, and steric hindrance.
By considering these factors, it is possible to select the appropriate reagent for a given reaction.
Reaction Mechanisms
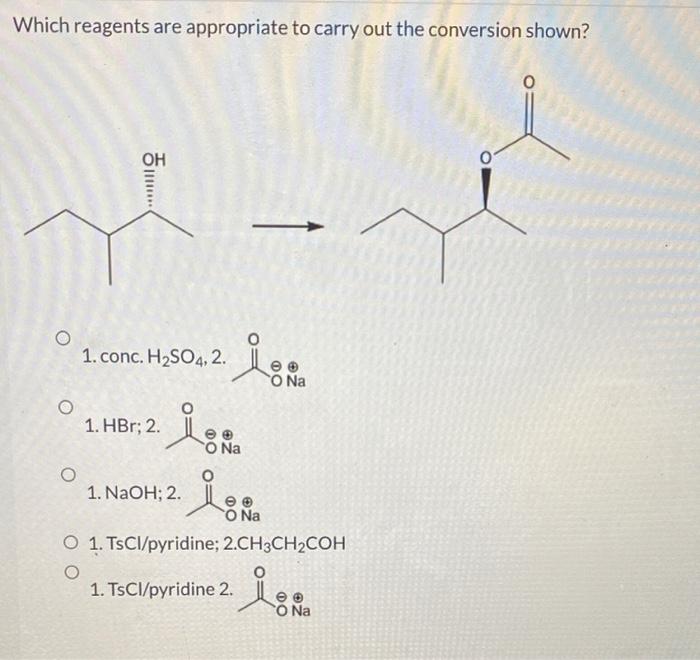
The mechanism of a reaction refers to the detailed step-by-step process by which a reaction occurs. The mechanism of a reaction can be determined by studying the kinetics of the reaction, the products of the reaction, and the intermediates that are formed during the reaction.
The choice of reagent can influence the mechanism of a reaction. For example, a nucleophilic reagent will react with an electrophile by a nucleophilic attack, while an electrophilic reagent will react with a nucleophile by an electrophilic attack.
The mechanism of a reaction can also be affected by the reaction conditions, such as the temperature, the solvent, and the concentration of the reactants.
Question Bank
What is the most important factor to consider when selecting reagents?
The most important factor to consider when selecting reagents is the functional groups present in the starting material and the product.
What other factors should be considered when selecting reagents?
Other factors that should be considered when selecting reagents include the reaction conditions, the desired yield, and the desired selectivity.
What is the best way to learn about reagents?
The best way to learn about reagents is to read books and articles about organic synthesis. You can also find helpful information online.