Introducing “The Supreme Court and Civil Rights Worksheet,” a meticulously crafted resource designed to illuminate the profound impact of the Supreme Court on the evolution of civil rights in the United States. This worksheet delves into landmark cases, contemporary issues, and the multifaceted role of the Court in shaping the legal landscape of equality and justice.
Through an in-depth examination of key cases and their enduring legacy, we trace the Supreme Court’s transformative influence on American society. From the groundbreaking Brown v. Board of Education to the recent Obergefell v. Hodges, the worksheet provides a comprehensive overview of the Court’s unwavering commitment to safeguarding civil rights.
1. Historical Overview of the Supreme Court and Civil Rights: The Supreme Court And Civil Rights Worksheet
The Supreme Court has played a pivotal role in shaping civil rights law in the United States. Through landmark decisions, the Court has interpreted the Constitution to protect the rights of all Americans, regardless of race, religion, gender, or sexual orientation.
Evolution of the Equal Protection Clause and Due Process Clause
The Equal Protection Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment guarantees equal protection under the law for all citizens. The Due Process Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment protects individuals from arbitrary or unfair government actions. Over time, the Supreme Court’s interpretation of these clauses has evolved to expand the scope of civil rights protections.
2. Key Cases and their Impact

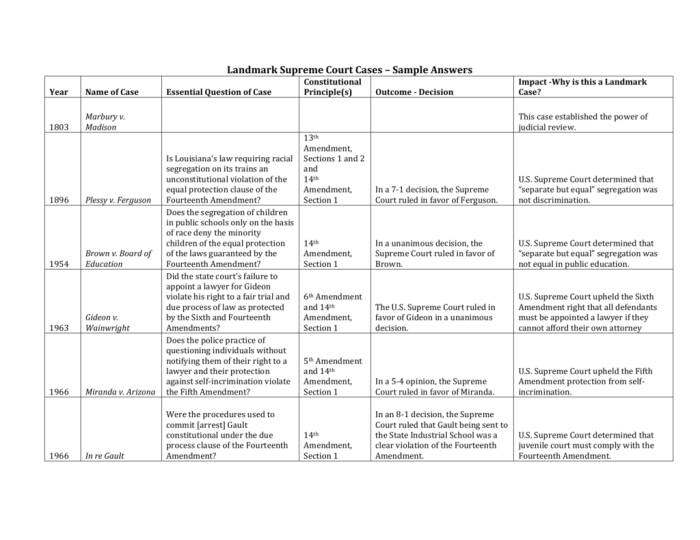
Brown v. Board of Education (1954), The supreme court and civil rights worksheet
This landmark case overturned the “separate but equal” doctrine and declared racial segregation in public schools unconstitutional. It paved the way for the desegregation of schools and marked a turning point in the civil rights movement.
Loving v. Virginia (1967)
This case struck down laws prohibiting interracial marriage, recognizing the fundamental right to marry regardless of race.
Obergefell v. Hodges (2015)
This case legalized same-sex marriage nationwide, affirming the right to marry for all couples.
3. Contemporary Issues and the Supreme Court
Affirmative Action
The Supreme Court has upheld the use of race-conscious policies in higher education to promote diversity and remedy past discrimination. However, it has also limited the scope of affirmative action programs.
Voting Rights
The Court has played a key role in protecting voting rights, upholding the Voting Rights Act and striking down discriminatory voting laws.
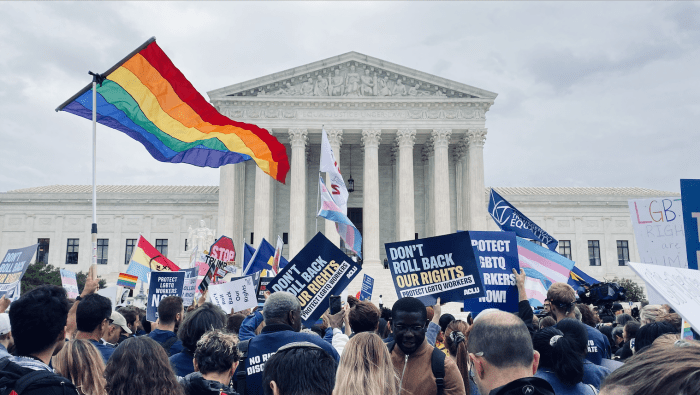
LGBTQ+ Rights
In recent years, the Supreme Court has extended civil rights protections to LGBTQ+ individuals, including the right to same-sex marriage and protection from employment discrimination.
4. The Court’s Composition and its Influence
The ideological makeup of the Supreme Court has a significant impact on its decisions on civil rights cases. Conservative justices tend to interpret the Constitution more narrowly, while liberal justices tend to adopt a more expansive view of civil rights.
Impact of Judicial Appointments
Presidential appointments to the Supreme Court can shape the direction of civil rights law for decades. Presidents often appoint justices who share their ideological views, which can have long-lasting implications for civil rights.
5. Comparative Perspectives on Civil Rights and the Supreme Court

In other countries, the role of courts in protecting civil rights varies. Some countries have constitutional courts that are specifically tasked with upholding fundamental rights, while others rely on ordinary courts or other mechanisms.
Lessons from International Perspectives
Comparing different legal systems can provide insights into the strengths and weaknesses of the American system of civil rights protection and suggest potential reforms.
Questions Often Asked
What is the significance of Brown v. Board of Education?
Brown v. Board of Education was a landmark 1954 Supreme Court case that declared state laws establishing separate public schools for black and white students to be unconstitutional. This ruling played a pivotal role in desegregating public schools and advancing the cause of civil rights in the United States.
How has the Supreme Court’s interpretation of the Equal Protection Clause evolved over time?
The Supreme Court’s interpretation of the Equal Protection Clause has undergone significant evolution. Initially, the Court applied a “separate-but-equal” doctrine, allowing for the segregation of facilities as long as they were deemed equal. However, in Brown v. Board of Education, the Court rejected this doctrine and held that separate facilities were inherently unequal.
Since then, the Court has continued to refine its interpretation of the Equal Protection Clause, extending its protections to a broader range of groups and contexts.
What is the role of the Supreme Court justices’ backgrounds and ideologies in shaping civil rights decisions?
The backgrounds and ideologies of Supreme Court justices play a significant role in shaping their decisions on civil rights cases. Justices with different backgrounds and experiences may bring diverse perspectives to the Court, influencing their interpretation of the law and their views on the role of the judiciary in protecting civil rights.